Last updated on 2024-07-29T22:23:06+08:00
发射光线和与光线三角形求交 发射光线 与 Whitted Style Ray Tracing 中的 Render 函数相同
1 2 float x = (2 * (i + 0.5 ) / (float )scene.width - 1 ) * imageAspectRatio * scale;float y = (1 - 2 * (j + 0.5 ) / (float )scene.height) * scale;
光线与三角形相交 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 inline Intersection Triangle::getIntersection (Ray ray) if (t_tmp < 0 )return inter;true ;Vector3f (u * v0 + v * v1 + (1 - u - v) * v2);ray (t_tmp);this ->m;this ;return inter;
happened:光线是否与三角形相交
coords:交点坐标
Ray重载了 () 运算符
1 2 3 4 Vector3f operator () (double t) const return origin + direction * t;
normal:三角形的法向量
distance:时间既是距离,即t_tmp
m:材质
obj:代表三角形本身
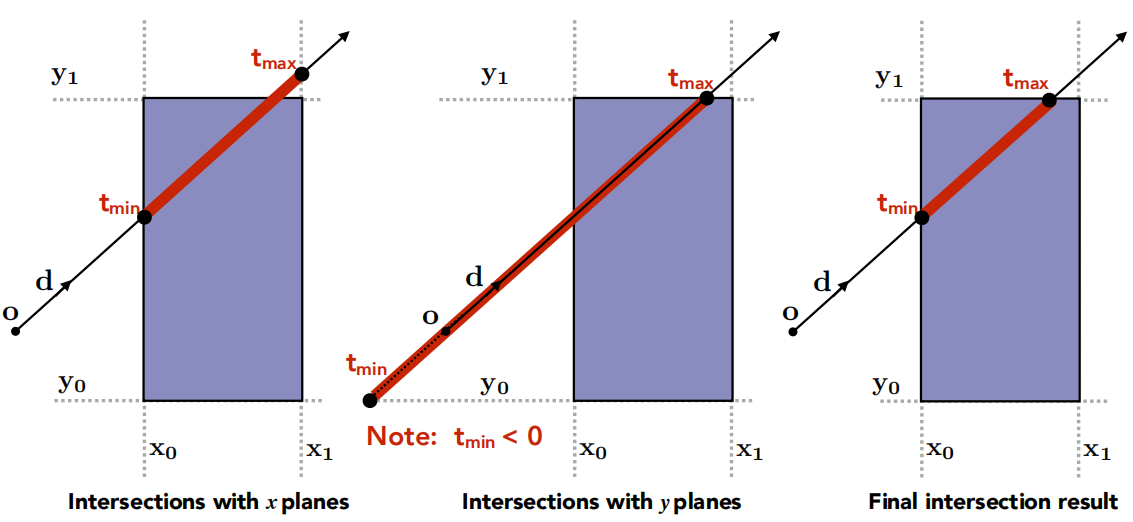
是否与包围盒相交
空间中的射线可以由起点
在三维空间中,使得光线经过包围盒的条件是:光线再包围盒上的两个点 插槽 里,即:dirIsNeg表示光线在某个方向上的投影是否为反向(例如当 dirIsNeg[1] == 0 时,表示光传播方向在
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 inline bool Bounds3::IntersectP (const Ray& ray, const Vector3f& invDir, const std::array<int , 3 >& dirIsNeg) const float tx_min = (pMin.x - ray.origin.x) * invDir.x;float tx_max = (pMax.x - ray.origin.x) * invDir.x;float ty_min = (pMin.y - ray.origin.y) * invDir.y;float ty_max = (pMax.y - ray.origin.y) * invDir.y;float tz_min = (pMin.z - ray.origin.z) * invDir.z;float tz_max = (pMax.z - ray.origin.z) * invDir.z;if (!dirIsNeg[0 ])float t = tx_min;if (!dirIsNeg[1 ])float t = ty_min;if (!dirIsNeg[2 ])float t = tz_min;float t_enter = std::max (tx_min, std::max (ty_min, tz_min));float t_exit = std::min (tx_max, std::min (ty_max, tz_max));if (t_enter <= t_exit && t_exit >= 0 )return true ;return false ;
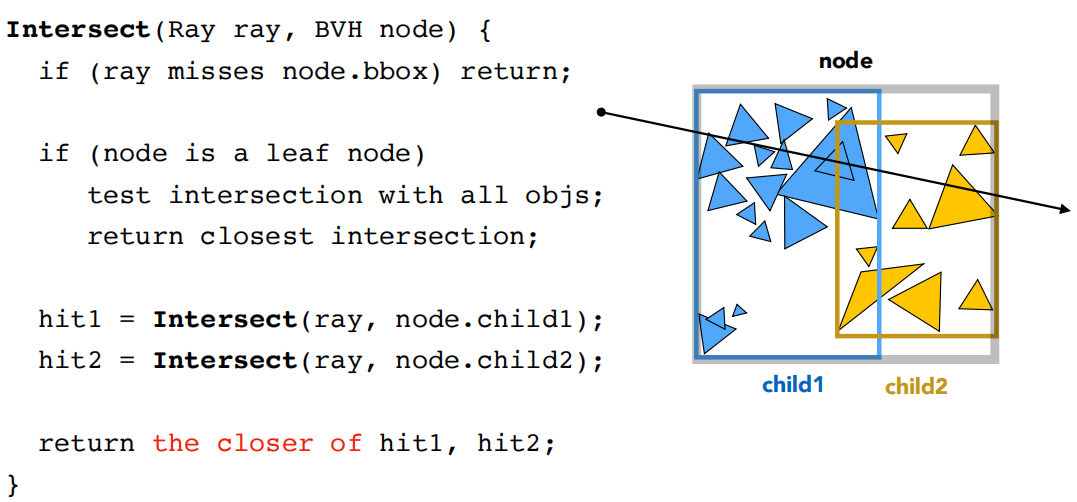
BVH Traversal BVH 本质上是把场景中的三角形用二叉树状的结构进行表示,中间结点包含这个结点所包含几何体的包围盒以及指向叶子结点的指针,叶子节点包含物体列表和包围盒,当判断光线与物体是否相交时,只需要递归的判断包围盒是否与光线相交即可 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Intersection BVHAccel::getIntersection (BVHBuildNode* node, const Ray& ray) const 1.0f / ray.direction.x, 1.0f / ray.direction.y, 1.0f / ray.direction.z };int , 3> dirIsNeg = {ray.direction.x > 0 , ray.direction.y > 0 , ray.direction.z > 0 };if (!node->bounds.IntersectP (ray, invDir, dirIsNeg))return {};if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr )return node->object->getIntersection (ray);getIntersection (node->left, ray);getIntersection (node->right, ray);return h1.distance < h2.distance ? h1 : h2;
结果